The radiology group practice CALW-Leonberg relies on SEARCH Lung CT from contextflow
Radiological diagnostics has continued to grow in recent years and is playing its part in improving patient care with ever greater precision. But this progress also has its downsides: Radiologists sift through and compare thousands of image slices from CTs and MRIs with increasingly better quality and thinner slices. This improved image quality is better for patients, of course, but it also results in more workload for radiologists. So what can be done to manage this workload in everyday radiology?
“We decided to purchase contextflow SEARCH Lung CT (software) for lung diagnostics, because the computer is an ideal tool to manage such challenges. All practices are under great economic pressure, and trends show that in the future, even more, not fewer, examinations will have to be managed in a shorter time,” says Dr. Ekkehard Scholtz, radiologist at the Calw and Leonberg radiology group practice, which serves not only outpatients there, but also offers radiology services as far away as Stuttgart. At the Calw location, outpatients are cared for in the city center; and in Leonberg, where the practice premises are located in the district hospital (Klinikverbund Südwest), the radiologists take care of outpatients and inpatients in the hospital.
At the radiology group practice in Calw-Leonberg, clinical routine includes not only standard examinations, but also high-resolution, thin-slice CT examinations used for the diagnosis of lung diseases and lung nodules. To better differentiate these diseases, the practice now uses software from contextflow.
Complexities of lung disease
In contrast to X-rays, which provide a very good but simple overview of the condition of the lungs, CTs provide high-resolution insights in the sub-millimeter range and thus enable the diagnosis of nodules, tumors, inflammations, malformations, injuries and fractures, including those of the ribs. “Despite all the technological and medical advances, lung disease remains a major challenge for us to this day. The renaissance of CT is also due to the fact that we can distinguish diseased lung very precisely, but unfortunately not one hundred percent. The patterns of the different types of lung disease overlap or mix, which makes it difficult to make a clear diagnosis,” explains Dr. Scholtz. “So we looked for software that could help us make a precise diagnosis. After all, the strength of AI is precisely to recognize patterns. In this respect, we are delighted to be using contextflow’s software.”
Expectations meet reality
CALW-Leonberg expects quantitative and qualitative improvements through the use of the new software. “Some days, our radiologists see between 20,000 and 30,000 high-resolution slices. In the case of the lungs, these are millimeter slices in three planes, so there are quickly up to 500 images that come together. These have to be viewed and, in some cases, compared with previous examinations. In addition, ILDs and any nodules must be measured. The AI is intended to help manage this workload. Qualitatively, it is a good inspection tool that sees findings that we might miss in routine clinical practice. Its use therefore provides better sensitivity and sensibility.”
So far, SEARCH Lung CT has delivered exactly what radiologists expected it to: more and better quality exams can be performed in less time. “We’re still in the early stages, and I estimate that when it’s fully functional, we’ll save about 30 percent of reading time with the new program. Above all, that means we will be able to help more patients,” says Scholtz confidently.
Where SEARCH Lung CT helps
Apart from the sheer mass of images to be processed, nodules and lung metastases have to be diagnosed and not only compared with previous examinations and older images in a high resolution, but also the nodules have to be measured manually with millimeter precision. This task can now be made easier with use of the software. Another aspect is pattern recognition, which plays such a big role in detecting lung diseases. The software helps to better differentiate the individual components of the various disease patterns that show up mixed or overlapping in the CT images. This is very important for targeted patient care, because there are lung diseases that end in fibrosis, a severe loss of function of the lung. Recently, however, therapeutics have come on the market that can influence the course of the disease and bring certain forms of fibrosis to a halt. In this respect, it is important to find out which form of fibrosis the patient is suffering from and whether they can be helped with these new therapeutic agents. So if it is possible to train pattern recognition in ILDs accordingly and thus obtain more differentiated statements, that will be a great benefit for patients.
How the system works
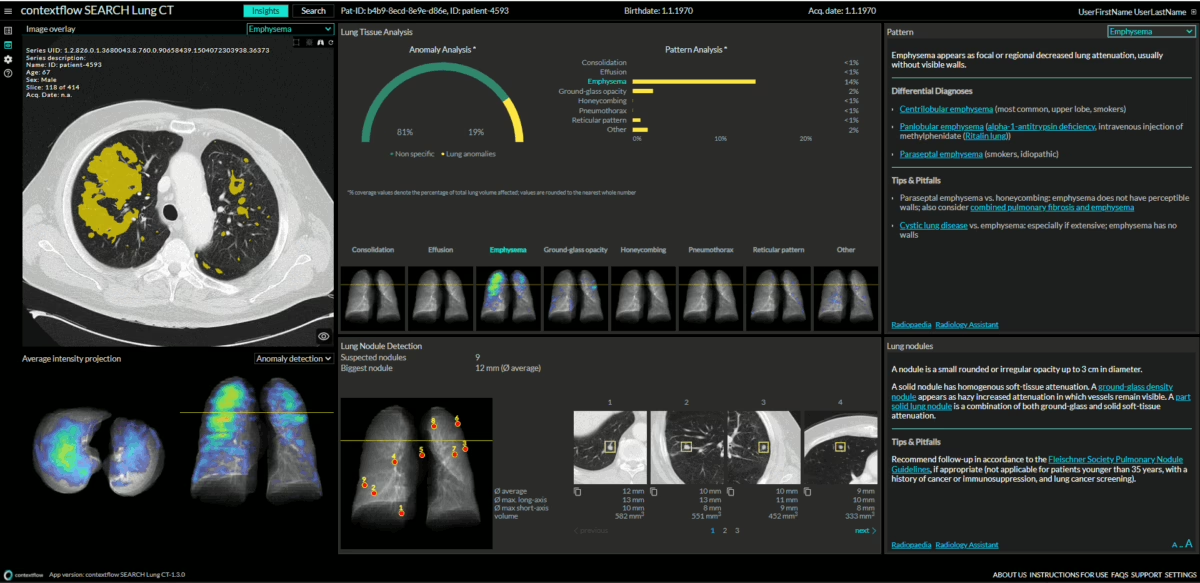
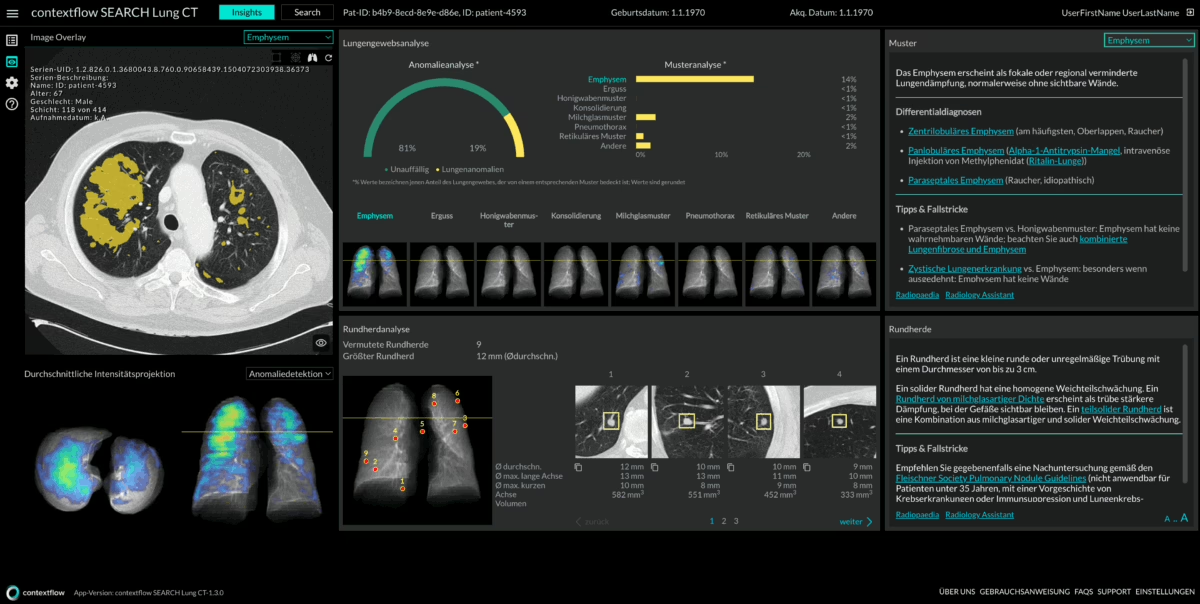
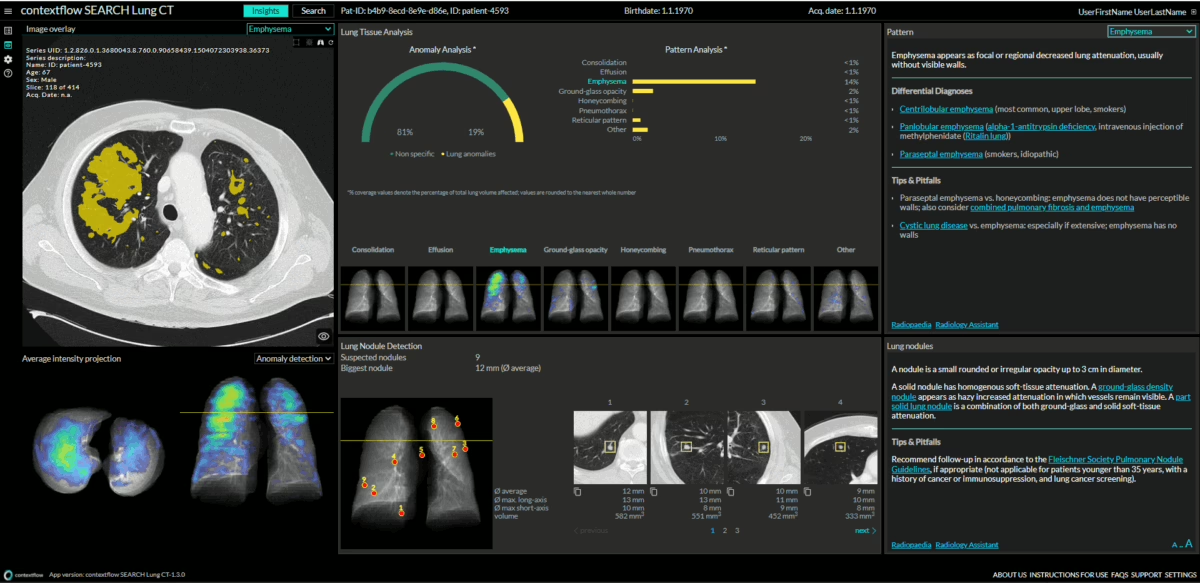
To use SEARCH Lung CT, the radiologist highlights an area of interest in a lung CT (in their native viewer), and then contextflow’s user interface opens in a new browser tab. “The home screen opens up and offers an analysis of the lung: disease patterns and nodules, their distribution and volume as well as a shortlist of possible diseases,” describes Scholtz. The radiologist takes over the evaluation of these measurements and suggestions, supported by heatmaps indicating the distribution of these disease patterns and their measurements by volume. An updated version of the software under development will display the disease patterns and nodules in enlarged form, measure their volume and then compare them with the disease patterns and nodules from the previous examinations. This is helpful because clinicians are most interested in how anomalies change over time in order to assess the patient’s treatment response. This is all the more challenging because there are often many nodules that also show contradictory behavior in that some get smaller while others get larger. At this point, the program is an invaluable help.
Smooth integration into existing IT
“Our goal from the beginning was to integrate SEARCH Lung CT into our existing IT infrastructure and not simply install another program. This process was challenging, but in the meantime the software has been integrated in such a way that we can activate SEARCH Lung CT from within our routine program,” Scholtz explains. The lung area to be diagnosed is marked in the radiologist’s viewer, and the finished analysis of the selected region is automatically generated as a PDF report. The prerequisite for this seamless integration was the very good cooperation between contextflow, our in-house IT and the IT provider Medigration from Bender Group, with whom CALW-Leonberg has been working for many years. “We work completely digitally – from the distribution of examination orders to the registration to the devices; from speech recognition, image and material management to dose management. There are a large number of sub-functions that converge in this system, and SEARCH Lung CT is one such deeply integrated sub-function.”
On a day-to-day clinical basis, radiologists are grateful for anything that saves time and improves diagnostics. “The system is perfectly integrated, and the workflow is so smooth that there is virtually no learning curve. We all use it automatically because we as diagnosticians get a real benefit for our patients,” says a satisfied Dr. Scholtz.
Looking toward the future
Since even the best solution still leaves something to be desired, contextflow is currently working on a feature that not only lists lung findings, but also compares them over time. In addition, the software is looking to move from the pattern-level to the disease-level, meaning it will also immediately provide suggestions as to which diseases these patterns may belong to for a given patient.