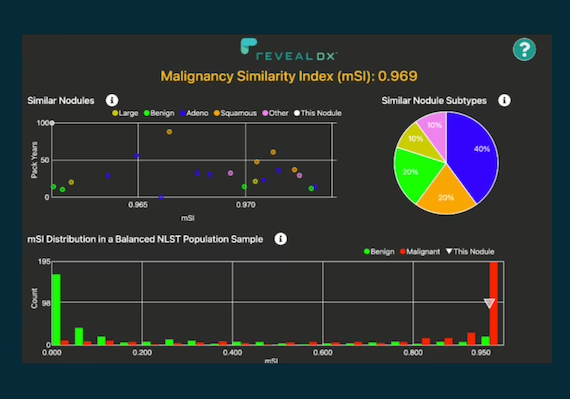
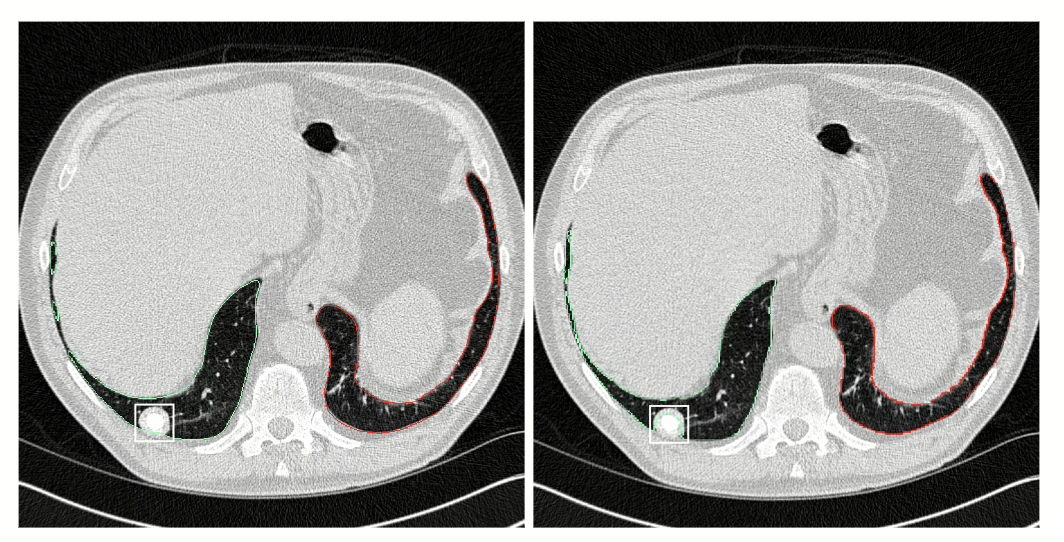
Les radiologues du groupe Imapôle Lyon-Villeurbanne bénéficient du support de l’IA de contextflow pour détecter les anomalies pulmonaires.
L’Imagerie Médicale, pilier central de la médecine moderne, est devenue incontournable aujourd’hui. Véritable pierre angulaire du diagnostic patient, elle le sera encore plus demain. Tourné vers le futur, Imapôle Lyon–Villeurbanne, le service d’Imagerie Médicale du plus grand établissement de santé privé de la région lyonnaise, le Médipôle Lyon-Villeurbanne, s’inscrit pleinement dans cette démarche et, dans cette optique, a intégré contextflow ADVANCE Chest CT dans sa routine clinique. Pour mieux comprendre les motivations de l’adoption de contextflow, les critères de sélection, l’expérience de déploiement et les bénéfices observés, nous avons rencontré Samir Lounis, CEO & General Manager chez ImaOne. Il dirige et pilote l’activité du groupe Imapôle.
Bonjour. Pourriez- présenter Imapôle Lyon-Villeurbanne ?
Le groupe Imapôle est composé de 10 radiologues. Ils sont chargés d’interpréter la production d’images médicales de deux sites : Le Médipôle Lyon Villeurbanne, le plus grand hôpital privé d’Europe avec plus de 850 lits, et le Pôle Médical d’OL Vallée à Décines.
Ces deux sites réalisent plus de 800 examens par jour et environ 170 000 examens par an.
Notre équipe gère cette charge de travail, et nous sommes fortement engagés dans l’utilisation de solutions d’intelligence artificielle.
Nous croyons fermement en leur potentiel pour soutenir nos radiologues et les transformer en « radiologues augmentés » grâce à l’IA, afin d’une part, pouvoir fournir des diagnostics plus précis et d’autre part, pouvoir gérer un volume d’examens beaucoup plus important.
Quelles ont été les motivations et les facteurs déterminants qui ont conduit votre département de radiologie à envisager l’adoption de l’application contextflow dans votre pratique clinique à Imapôle Lyon-Villeurbanne ?
Au sein d’Imapôle, une part importante de notre activité concerne la cancérologie, environ un tiers. Cela implique que nous devons interpréter un grand nombre d’images, en particulier des scanners, pour le suivi ou la détection de pathologies chez nos patients.
Dans ce contexte, nous avons cherché une solution qui puisse nous aider à dépister les lésions et à suivre leur évolution en termes de taille, notamment en ce qui concerne la croissance ou la diminution des lésions.
Mesurer une lésion est une tâche complexe et sujette à de nombreuses variations. Cela dépend du plan de coupe utilisé pour la mesure et de l’inclinaison de la lésion elle-même, par exemple dans le cas d’une lésion pulmonaire.
De nombreux facteurs entrent en jeu. Nous souhaitions donc que cette mesure puisse être volumétrique et reproductible.
Partant de tous ces éléments, nous avons décidé d’utiliser un logiciel. Nous sommes également impliqués dans un programme de dépistage du cancer du poumon au sein du Médipôle.
En France, des études sont actuellement menées dans ce domaine. Au sein d’Imapôle Lyon Villeurbanne, nous disposons d’un département de pneumologie important et nous avons voulu proposer une solution reproductible, efficace et indépendante de l’opérateur qui se trouve derrière l’écran.
Parmi les différentes solutions que nous avions identifiées, le logiciel de contextflow, qui figurait parmi les trois finalistes, nous a paru être le plus performant et le plus complet, répondant ainsi à nos besoins.
Quels ont été les critères de sélection et les évaluations préliminaires effectués avant de choisir l’application contextflow pour votre département de radiologie ?
Nous avons exploré le marché pour rechercher des solutions adaptées à notre mission, qui consiste à détecter et suivre les lésions pulmonaires dans le temps, tout en tenant compte d’autres critères tels que le délai de retour des résultats. Il était essentiel que l’analyse puisse être réalisée rapidement, avec un retour dans le PACS et vers le médecin dans un délai de l’ordre d’environ cinq minutes, afin de maintenir notre flux de prise en charge des patients. Après avoir comparé contextflow à d’autres fournisseurs, nous avons choisi contextflow parce qu’il offre plus que la simple détection de nodules et qu’il s’intègre très bien dans notre PACS.
L’autre point qui a été un « game changer » dans notre choix, c’est la capacité de contextflow à pouvoir se projeter et proposer, dans un avenir proche, la détection des embolies pulmonaires fortuites.
Nous disposons ainsi d’un outil capable de répondre à plusieurs de nos problématiques, notamment en cancérologie, pour le suivi à long terme, l’analyse et la reproductibilité des mesures, ainsi que l’analyse et la quantification d’autres pathologies pulmonaires comme l’emphysème.
Pouvez-vous retracer l’historique de l’intégration de l’application logicielle contextflow dans votre département de radiologie, depuis sa mise en place jusqu’à aujourd’hui ?
Les équipes techniques de contextflow ont été extrêmement réactives. Nous avons pu les mettre en relation avec nos équipes IT et PACS, et les trois équipes ont rapidement réussi à installer la machine virtuelle pour effectuer tous les tests. Nous avions un délai assez court pour atteindre un niveau d’intégration qui nous permettrait une utilisation transparente, sans que le médecin ne quitte son environnement. C’était un élément clé.
La solution contextflow est entièrement intégrée dans notre flux de travail. Les envois se font automatiquement de la modalité vers la solution d’IA, et les résultats sont renvoyés dans le PACS. Ainsi, lorsque le médecin prend connaissance de l’examen, il dispose des résultats de contextflow.
L’accompagnement technique et le support des équipes lors du démarrage ont été extrêmement réactifs, ce qui est très positif pour contextflow. Le niveau d’intégration avec notre PACS est très élevé.
Quelles ont été les étapes clés du processus de mise en œuvre de l’application contextflow dans votre département de radiologie en termes de formation, de personnalisation et de gestion du changement ?
En ce qui concerne contextflow, la formation s’est déroulée en deux étapes. Tout d’abord, il y a eu une formation préliminaire qui consistait essentiellement en une présentation du produit, puis une deuxième partie où l’application du produit a été présentée. Nous avons examiné un cas concret et analysé les résultats obtenus. Cette formation a été dispensée en visioconférence à différentes dates, afin de convenir aux disponibilités des différents médecins impliqués dans le projet, ce qui a été très apprécié.
Nous avons pu démarrer l’utilisation de la solution avec un accompagnement à distance, si nécessaire, tant de la part de l’équipe de contextflow que de notre équipe IT et PACS. Tout s’est très bien passé.
Après environ un mois d’utilisation, contextflow nous a proposé d’accompagner nos équipes médicales sur site, afin de bénéficier de leur expérience. Cela permettrait également d’apporter des ajustements personnalisés à l’utilisation du produit et de leur faire découvrir des fonctionnalités qu’ils n’auraient peut-être pas saisies lors des premières formations.
Cet accompagnement est toujours en cours. Nous aurons un technicien de l’application qui viendra la semaine prochaine pour rencontrer nos équipes. Il pourra également revenir si les médecins en ressentent le besoin. Maintenant, en ce qui concerne contextflow, le gros avantage est qu’ils ne se limitent pas à la détection et au suivi des nodules dans le temps, ce qui est essentiel et très important pour le dépistage du cancer du poumon, par exemple, et le suivi des fumeurs. Mais, au contraire, il permet aussi d’analyser d’autres pathologies, notamment l’emphysème, ce qui est une quantification primordiale, surtout dans une perspective d’avenir.
À l’avenir, il permettra également de détecter les embolies pulmonaires fortuites, un diagnostic crucial en radiologie. Au Medipôle Lyon Villeurbanne, le plus grand service d’urgence privé de France, nous recevons environ 250 patients par jour, dont la moitié environ passe par le service d’imagerie, et beaucoup d’entre eux bénéficient d’un scanner.
Nous sommes très heureux d’être soutenus par un logiciel de détection basé sur l’IA pour ces 250 patients, car la charge de travail des radiologues ne cesse d’augmenter. On se retrouve avec 400 à 500 images à analyser par patient. C’est donc une bonne chose d’avoir une intelligence artificielle qui peut vous accompagner dans cette phase de détection et mettre en évidence les zones à risque.
C’est pourquoi la capacité de contextflow à prendre en charge de nouvelles pathologies à analyser a également été un facteur déterminant dans le choix de la solution.
Comment l’application contextflow a-t-elle été intégrée dans le système d’information radiologique existant à l’Imapôle, pour assurer la compatibilité, l’interopérabilité et la synchronisation des données cliniques ?
Ce qui est le plus important, c’est toute la phase préparatoire d’intégration. Cela nécessite un travail considérable qui s’étend sur quelques semaines, pendant lesquelles tous les acteurs impliqués peuvent échanger sur les contraintes techniques. L’utilisateur final, notamment le médecin, peut exprimer ses attentes et objectifs, en particulier sur la manière dont il souhaite retrouver les résultats dans son flux de travail.
La réussite de cette étape se traduit par le fait que, finalement, le médecin n’a pas besoin de quitter son environnement de travail habituel. Il ouvre son PACS et y travaille – les résultats contextuels sont là sans avoir à ouvrir un nouveau programme ou à changer de fenêtre. L’utilisateur n’est pas confronté à une interface totalement différente. En outre, les résultats de contextflow peuvent être adaptés par le radiologue en cas de désaccord, par exemple dans le cas d’un nodule faussement positif.
Plus on parvient à apporter de transparence dans l’utilisation de contextflow au sein du PACS, plus l’intégration est réussie et plus le médecin l’utilisera régulièrement.
Comment mesurez-vous la satisfaction globale des utilisateurs de l’application contextflow au sein de votre département de radiologie en termes de convivialité, de performance et de contribution à la prise de décision clinique ?
Chaque clic coûte du temps et de l’argent aux radiologues, c’est pourquoi il était prioritaire pour nous d’avoir une solution d’IA bien intégrée avec le moins de clics possible.
C’est un élément clé dans l’utilisation de la solution.
Si l’on propose à un médecin, qui est déjà très occupé et soumis à une charge mentale importante liée à l’analyse médicale, des contraintes supplémentaires telles que de devoir naviguer entre différentes fenêtres ou dossiers, il est certain que la solution ne sera pas utilisée. Il peut l’essayer une ou deux fois, mais rapidement, il se rendra compte que cela lui prendra du temps et il finira par se dire : « Je vais m’en passer » et il n’y reviendra plus.
En revanche, si l’on automatise l’ensemble du processus, c’est-à-dire que les images sont acquises par le scanner, envoyées automatiquement à l’IA de contextflow pour analyse, que les résultats sont renvoyés au médecin dans son environnement de travail et qu’il n’a plus qu’à valider ou invalider les résultats de l’IA pour les intégrer dans son compte rendu, alors le nombre de clics est réduit au minimum.
Cela permet une convivialité très appréciable. De plus, le degré d’intégration de la solution dans notre PACS est extrêmement poussé, ce qui rend notre dépendance à la solution encore plus bénéfique.
Quels sont les indicateurs de performance et les critères d’évaluation utilisés pour mesurer l’efficacité et l’impact clinique de l’application contextflow dans votre département de radiologie ?
Au niveau de nos prescripteurs, nous avons une grande quantité de pneumologues et de pneumologues-oncologues au sein de notre pôle. Nous avons donc une équipe de médecins spécialisés dans les affections pulmonaires. Ils ont été très satisfaits de l’application contextflow à un niveau avancé de l’analyse pulmonaire, notamment ici à Lyon. Ils ont particulièrement apprécié la capacité de détecter et de suivre les pathologies pulmonaires dans le temps, ainsi que la possibilité de comparer les résultats.
Lorsqu’un patient est envoyé pour une évaluation après trois ou six mois de chimiothérapie, il est extrêmement précieux de disposer d’un outil tel que contextflow pour assurer la reproductibilité de l’analyse et des mesures. Cela a réellement été un atout majeur pour nos médecins prescripteurs.
Aujourd’hui, l’utilisation de l’outil est demandée presque systématiquement par les médecins prescripteurs, car ils se sont habitués à son utilisation. Ils orientent donc leurs patients vers notre centre afin que leurs examens puissent bénéficier de cette analyse complémentaire en interne. En ce qui concerne nos propres médecins, comme je l’ai mentionné précédemment, plus l’interface dans le flux de travail est transparente, plus elle est utilisée.
Ainsi, à l’heure actuelle, 100 % des scanners pulmonaires passent par contextflow, bénéficiant ainsi d’une double analyse à la fois médicale et assistée par IA.
Les retours que nous avons obtenus en discutant avec les médecins montrent clairement que l’outil a été adopté et utilisé de la même manière que d’autres outils d’IA que nous avons dans notre parc. Nous avons une équipe de médecins précurseurs dans l’adoption de l’IA, et ils sont conscients des avantages que peut leur apporter l’intelligence artificielle.
Comment aimeriez-vous que la solution contextflow évolue à l’avenir ?
J’aimerais beaucoup que contextflow apporte une solution pour la détection d’embolie pulmonaire, car c’est un besoin réel pour tous les services d’imagerie médicale d’urgence. Cela aidera considérablement les urgentistes et les médecins, accélérant ainsi la prise en charge des patients et réduisant le temps perdu lors de l’analyse. L’équipe de contextflow a pris nos remarques au sérieux et travaille dans ce sens.
Nous sommes très satisfaits de la solution actuelle. contextflow améliore continuellement la spécificité et la sensibilité de l’algorithme de détection des nodules. Ensuite, nous envisageons d’étendre les possibilités d’analyse des pathologies thoraciques, pas seulement pour les poumons, mais également pour les vaisseaux et le cœur, ainsi que pour tous les organes situés dans la région thoracique.
Si à l’avenir, contextflow pouvait également fournir une analyse pour ces éléments, ce serait un véritable atout.
L’IA est considérée comme l’avenir, mais elle suscite également des craintes. En tant qu’utilisateur, vous pouvez être à la fois enthousiaste et réticent vis-à-vis de certaines applications. Cependant, en tant qu’être humain, vous êtes conscient des implications et des limites de l’IA. Cela peut ouvrir la porte à diverses possibilités. Quelle est votre opinion sur ce sujet ?
Dans notre monde où tout évolue rapidement, bien plus rapidement que la capacité d’adaptation d’un être humain, les données, qu’elles soient médicales ou non médicales, sont multipliées de façon exponentielle. L’analyse de ces données doit donc également être multipliée.
Cependant, les êtres humains n’ont pas la capacité d’adaptation instantanée à un tel flux de données. Peut-être serons-nous capables de le faire dans X années, mais aujourd’hui, nous avons besoin de solutions qui nous accompagnent dans la gestion de ce flux de données. Il est crucial de trier et d’analyser ces données et informations.
En ce qui me concerne, je peux dire que l’IA peut susciter des inquiétudes sur certains aspects. Cependant, je pense que l’IA ne remplacera pas les médecins. C’est un fait que j’ai expérimenté en utilisant ces solutions depuis plusieurs années et en les observant dans notre pratique.
En revanche, ce qui est certain, c’est que le médecin qui utilise l’IA remplacera le médecin qui n’utilise pas cette technologie. C’est là que réside le véritable enjeu. Le monde a évolué plus rapidement que la capacité d’adaptation de l’être humain. Il a donc besoin d’outils technologiques. Ainsi, le médecin qui intègre l’IA dans sa pratique surpassera le médecin « tout court ».